Environmental health is one field of public health that takes into account environmental aspects in relation to health issues. World Health Organisation (WHO) definend environmental health as:
“Those aspects of human health and disease that are determined by factors in the environment. It also refers to the theory and practice of assessing and controlling factors in the environment that can potentially affect health”
Or simply said, an ecological balance must exist between humans and the environment in order to guarantee the healthy condition of humans.
As explained by Hendrik L. Bloom, among the four determinants of health status, the environment is one of them. Note also that this neighborhood has the most impact on health.
Also read: HL Bloom Theory in Public Health Sciences
There are four types in environmental components, namely:
- Physical: Water, Air, Weather, Radiation
- Chemical: Smoke, Pesticides, Hazardous Waste
- Biology: Germs, Bacteria, Viruses
- Social: Economy, Politics, Culture
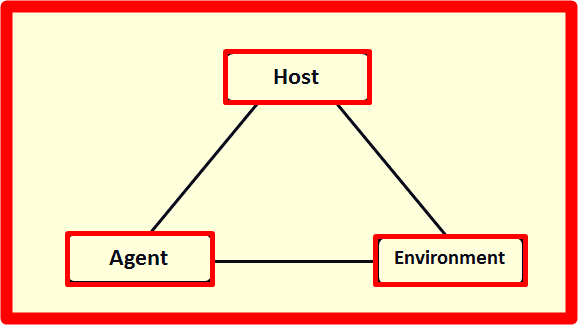
Agent – Host – Environment in Environmental Health
Humans in their daily lives cannot be separated from interactions with the environment. Starting from air, water, other facilities and infrastructure to interactions related to the social and cultural environment.
Therefore, the theory of epidemiology triangle agent – host – environment describe the interaction of all three.
- Host, in this case it is human.
- Agent, that is, the source of the disease.
- Environment, is the place in which to interact.
Also read: What is Epidemiology in Public Health?
If there is an imbalance in the triangle, then the possibility of health problems will arise where the environment plays an important role.
Therefore, environmental health function is important to identify and evaluate environmental resources and harmful agents.
Also its function to take protective measures by managing exposure to hazardous physical, chemical and biological agents from air, water, soil, food and other media that can affect human health.
Notes from DeveHealth:
Because human interaction with the environment is unlimited. Then the scope of environmental health had become very broad.
Some of the examples are drinking water supply, waste management, vector control, food hygiene, air pollution control, aspects of housing and settlements up to a recreation or tourism.
Also read: Health Promotion Challenges during COVID-19 Pandemic




